
![]()
Using the Box Model
From the perspective of a style sheet, every item you deal with in an HTML page can be viewed as existing inside a box. This fact is generally far more obvious when you are formatting large chunks of content, like a block of links, or a division on a page. But it's true even when you're dealing with indiviual components of those elements, like headings, lists, list elements, and even segments of text.
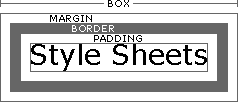 The
basic CSS box model is illustrated at the right.
The
basic CSS box model is illustrated at the right.
- The content is located in the center of the model. Don't think of the content as being text only; content can be anything that is contained within the area of the box, such as images, links, or a division of a page.
- Padding is the distance between the content and the location of any border (if you add one).
- The Border is a decorative container for the content. It is placed between the padding and the margin.
- The Margins determine the distance between each side of the visible box and other content left and right, and between the visible box and other content above and below.
- The visible width of the box on the page is determined by adding together the width of the content, the padding and the border. The margin is the space outside of this visible width, which creates negative space on your page, making it easeir to read.
The width of each of these elements - padding, margin and border - can be set using four CSS properties (one for each side of the box), or with a single shorthand property. Border behavior is slightly more complicated, as the border can also have characteristics of style and color. These differences will be discussed in the border properties section.
Box Measurement Units
The measurement units used to define the widths of the box elements may be expressed in either absolute or relative measurments.
The pixel is the most commonly used of the absolute measurements units in CSS. This is because the box model deals with the display of content on the screen, so you usually want specific sizes for the spacing.
However if you are creating a layout should keep the same proportions, regardless of the browser window size, it is necessary to use relative measurments, usually ems or percentages.
Padding Properties
The four properties that define the padding around an object in a CSS rule are:
- padding-left
- padding-right
- padding-top
- padding-bottom
You can use just one, or any combination of these properties in a rule to define the space around your content as you wish. For example:
p { padding-left: 25px;
padding-top: 10px;
}
You can also use the shorthand property, which will set padding depending on how the values are arranged:
- padding
There are four different ways to use the padding shorthand property, by giving 1, 2, 3, or 4 values. The different number of values work in the following way:
| Number of values | Example | Interpretation |
| 1 | p { padding: 25px; } | Set all four padding values to this value |
| 2 | p { padding: 20px 25px; } | Set the top and bottom to the first value and the left and right to the second value |
| 3 | p { padding: 10px 25px 20px; } | Set the top padding to the first value, the right and left to the second value, and the bottom to the third value |
| 4 | p { padding: 15px 20px 30px 25px; } | Set the top padding to the first value, the right padding to the second, the bottom padding to the third, and the left padding to the fourth value (the order is clockwise from the top) |
Margin Properties
The difference between margins and padding is that the margins exists outside the boundaries of the visible object, while padding exists inside the boundaries.
The margin properties work in exactly the same way as the padding properties, with four properties for the four sides of the box, as well as a shorthand property that can combine the settings.
For horizontally placed objects - If you have two content elements arranged horizontally, all margins will be applied to both. This means that if you have a 25px margin on the left and right, there will really be 50 pixels of space between your objects.
For vertially placed objects - Two content elements arranged vertically will not apply margins int he same way as for left and right. If you have 10px of space top and bottom on two objects that are adjacent vertically, the spacing will be the larger of the two settings, not the two combined.
It is also possible to use negative values in margin settings, in order to override default settings where you want to.
Margins in lists
By default, all browsers will apply a 50-pixel spacing to the left edge of a list. This allows room for the list item markers (bullets, numbers). Unfortunately, the CSS specification does not say whether this space should be padding or margin by the browers default style rules. Some browsers apply margin, some apply padding.
For this reason, whenever you apply your own left margin or padding values to a list, you should be sure to specify both, in order to guarantee the effect you want.
Border Properties
Border properties are more complex than padding and margin properties because they affect not only the spacing between objects, but the appearance of that space too. A border is usually visible, and its style and color must also be set. Most of the border properties are like padding and margins, but there are some differences, as described below.
Borders have three types of properties: style, width and color.
By default,
a border's style is set to none, its width to medium, and its color to
the text color of the HTML element to which it is applied.
border-style Properties
Border styles are set by separate properties as with padding and margins:
- border-top-style
- border-right-style
- border-bottom-style
- border-left-style
There is also a border-style shorthand property that can combine the four settings, as described in the section on padding, to set the same border style on all four sides at the same time.
|
|
These properties can take any one of a range of constant values. The available values are listed at the right. The hidden value is the same as none, except when applied to table elements. The appearance of the various border styles can vary somewhat between browsers.
border-color Properties
The border colors are also set by four separate properties:
border-top-color,
border-right-color, border-bottom-color, border-left-color
There is also
the border-color shorthand property to set
one to four properties at the same time..
Values for the border-color properties
may be names, hex codes or rgb settings.
border-width Properties
The border widths are also set by four separate properties:
border-top-width,
border-right-width, border-bottom-width, border-left-width.
There is
also a border-width shorthand property that can combine the settings.
The width values can be:
- absolute values - pixels, inches, etc.
- relative values - ems, %, etc.
- one of three descriptive values: thin, medium, or thick. These descriptive settings are browser dependent for their actual values.
If you want specific border setting, it is best to use pixels, especially when you are defining screen layouts that you want to look the same on all computers.
Border Shorthand Properties
In addition to the normal shorthand properties that will set all four sides of the style, width or color at the same time, there are also shorthand properties which will set all three properties - width, style, color - for one side at the same time.
For example, you could use the border-top property to set the thin, double and red all at the same time with the following declaration:
border-top: double red thin;
There is also the shorthand property that will set all properties for all four sides at once.
The following declaration will set all four borders to a thick blue inset style.
border: inset blue thick;
The order matters for the shorthand border properties. If you are using any of the shortcut properties that combine style, color and width, you must list them in that order: style first, color second, and width third.
A Word about Shorthand Properties vs Individual Properties
You might ask at this point why to use individual properties to control the sides of your 'boxes'. Often a shorthand property will be used in the body or other tag style, setting all four sides of the boxes alike. Then a class may be applied to change one or more of the sides individually for particular effects where they are desired. For example, you can set the margins of the body to 0.5in, then set the margin of a header as -0.25 in, to make that header different - more to the left than the other elements - only where you want this effect.
Many designers prefer to use individual properties in order to be sure of all settings. If everything is specified, then there are no questions as to what the page might look like on different browsers with different default settings.
Below is a reference for all box properties, showing the possible values.
| Property | What it does | Possible values |
| padding-top | Adds top padding | by length | by percentage | auto |
| padding-right | Adds right padding | by length | by percentage | auto |
| padding-bottom | Adds bottom padding | by length | by percentage | auto |
| padding-left | Adds left padding | by length | by percentage | auto |
| margin-top | Specifies a top margin | by length | by percentage | auto |
| margin-right | Specifies a right margin | by length | by percentage | auto |
| margin-bottom | Specifies a bottom margin | by length | by percentage | auto |
| margin-left | Specifies a left margin | by length | by percentage | auto |
| border-top-style | Specifies a top border style | inset | outset | ridge | solid | double | groove | dashed | dotted | none |
| border-right-style | Specifies a right border style | inset | outset | ridge | solid | double | groove | dashed | dotted | none |
| border-bottom-style | Specifies a bottom border style | inset | outset | ridge | solid | double | groove | dashed | dotted | none |
| border-left-style | Specifies a left border style | inset | outset | ridge | solid | double | groove | dashed | dotted | none |
| border-top-color | Sets the top border color | color by name, hexcode or rbg values |
| border-right-color | Sets the right border color | color by name, hexcode or rbg values |
| border-bottom-color | Sets the bottom border color | color by name, hexcode or rbg values |
| border-left-color | Sets the left border color | color by name, hexcode or rbg values |
| border-top-width | Sets the width of the top border | thick | medium | thin | by length (measurement) |
| border-right-width | Sets the width of the right border | thick | medium | thin | by length |
| border-bottom-width | Sets the width of the bottom border | thick | medium | thin | by length |
| border-left-width | Sets the width of the left border | thick | medium | thin | by length |
| border-top | Defines all values for a top border with one declaration | style | color | width |
| border-right | Defines all values for a right border with one declaration | style | color | width |
| border-bottom | Defines all values for a bottom border with one declaration | style | color | width |
| border-left | Defines all values for a left border with one declaration | style | color | width |
| border | Defines identical values for all four sides with one declaration | style | color | width |
padding (with 1 value) |
Uses shorthand to specify all four sides to have the same value(s) | |
padding (with 2 values) |
Uses shorthand to specify top and bottom to one value, and left and right to another value | |
padding (with 3 values) |
Uses shorthand to specify the top as one value, left and right as another value, and bottom as a third value | |
padding (with 4 values) |
Uses shorthand to set all four sides to different values |